Java文件字符输入流FileReader读取txt文件乱码问题
本文共 799 字,大约阅读时间需要 2 分钟。
先上代码:
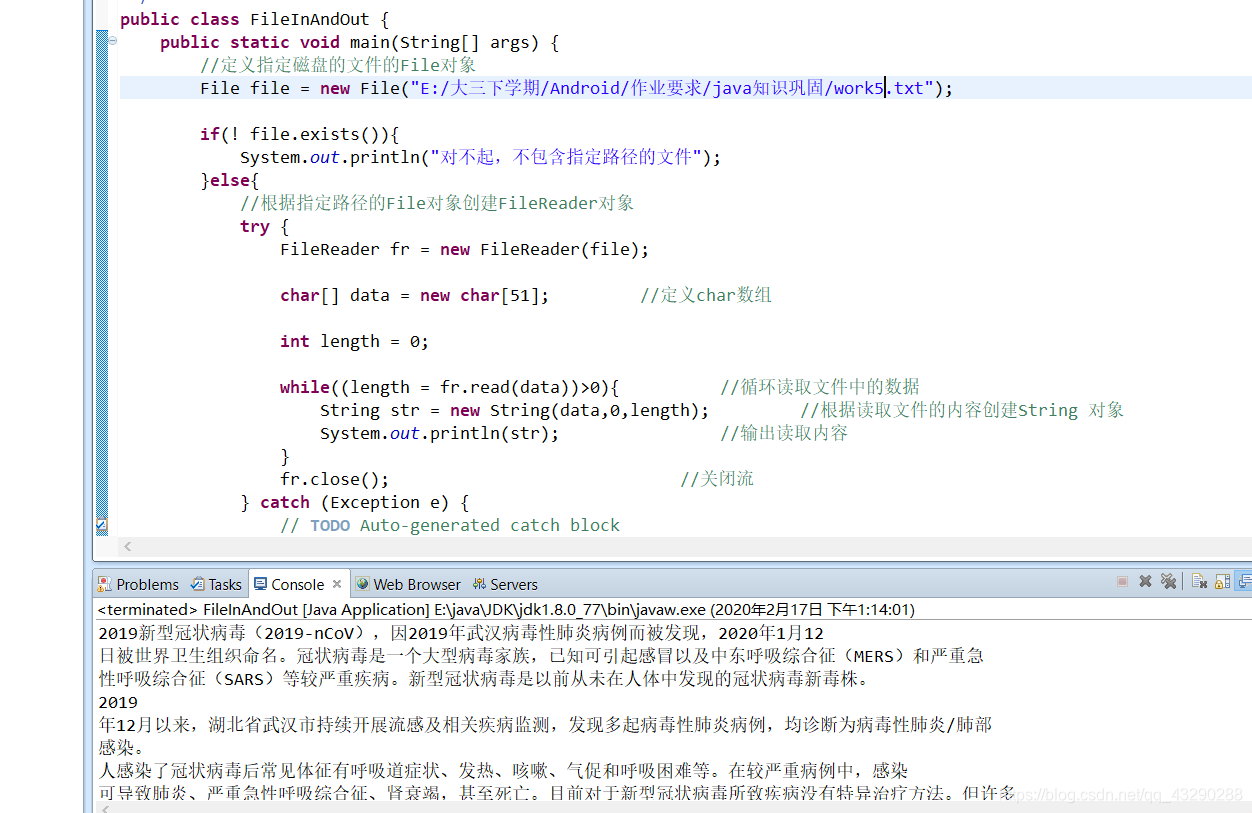
public class FileInAndOut { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义指定磁盘的文件的File对象 File file = new File("E:/大三下学期/Android/作业要求/java知识巩固/work5.txt"); if(! file.exists()){ System.out.println("对不起,不包含指定路径的文件"); }else{ //根据指定路径的File对象创建FileReader对象 try { FileReader fr = new FileReader(file); char[] data = new char[51]; //定义char数组 int length = 0; while((length = fr.read(data))>0){ //循环读取文件中的数据 String str = new String(data,0,length); //根据读取文件的内容创建String 对象 System.out.println(str); //输出读取内容 } fr.close(); //关闭流 } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }} 控制台输出结果如下:

原因是
Java中的字符流处理的最基本的单元是Unicode码元(大小2字节),所以,我们在保存的时候要将文件的编码格式改为utf-8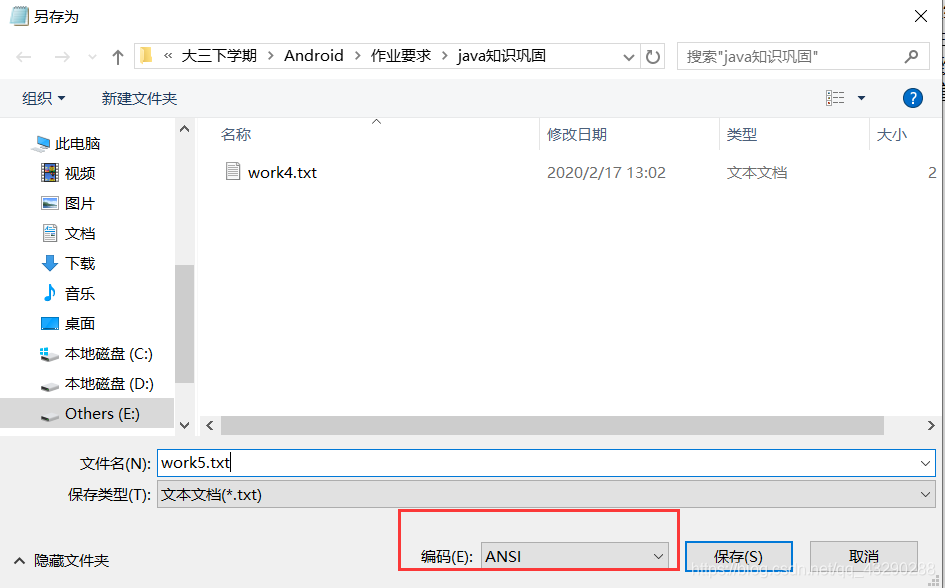
运行之后的结果为
转载地址:http://cooq.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章